
Did your email bounce?
Annoying, I know.
We take email for granted these takes. Just hit send and walk away. Unfortunately, sometimes things do go wrong, and you get that ugly email bounce in your inbox.
If this is an email to a friend, you can always send an SMS. What if this is a marketing campaign? Your job or business may depend on your emails reaching your contact list.
Below we’ve assembled everything you need to know about bounced emails. If you are ready to keep your email flowing, keep reading.
From the basics to bounce handling strategy, we have it covered.
Table of Contents
- What is an email bounce?
- How do I recognize and email bounce?
- Details of an Email Bounce
- Type of Email Bounces
- Hard Email Bounces
- Soft Email Bounces
- Email Bounces Impact Deliverability
- How to Fix a Bounced Email
- Getting Email Headers
- SMTP Error Code Reference
- Summary & Help
What is an email bounce?
An email bounce is simply an email that cannot be delivered. For various reasons, email servers may reject emails you send.
When a server rejects and email, the system sends you a bounce, technically known as a Non-Delivery Report. For you tech geeks, take a look at RFC 5321.
How do I recognize an email bounce?
Depending on the type of email server and client, your email bounce notification may have different From addresses and Subject lines.
For example, Gmail bounces look like this.
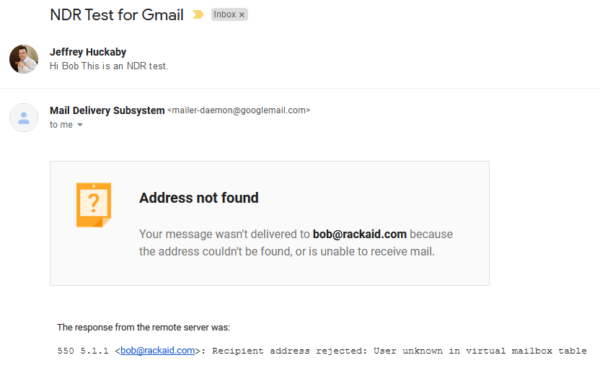
In Thunderbird, you may see this:
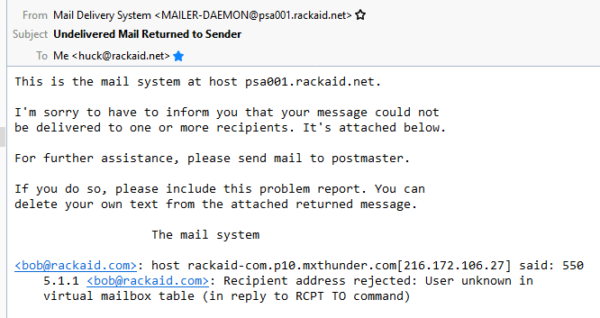
In Windows 10 Mail App, you may see this:
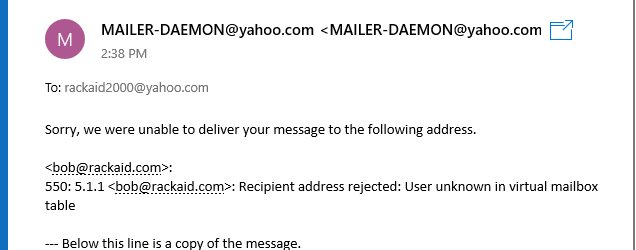
Regardless of the From and Subject lines, if you see these errors, your message did not reach the recipient.
Details of an Email Bounce
Bounce notices contain important information about why the email bounced.
Bounces typically include:
- A message ID unique to your email.
- The time and date the message bounced.
- The email server’s IPs and hostnames.
- The SMTP error code.
- The error message.
Don’t delete the bounce. Your email administrator can use these details to identify why you cannot send the email.
Types of email bounces?
There are two categories of email bounces: Hard and Soft. Depending on the email service you use, the bounce notice may mention a permanent failure. A permanent failure is a hard bounce. Temporary failure is a soft bounce.
Hard Email Bounces
A hard bounce is a permanent failure. Permanent failures are just that – permanent. The server was unable to deliver the email and has stopped trying to send the message. The error code for a hard bounce is 550. If you see 550 in your bounce email, you have a hard bounce.
Reasons for Hard Bounces:
- Unknown user errors.
- Unknown domain errors.
- Email block by the server due to spam filters.
- Email blocked by the server due to policy filters.
- Your attachment type is too-large or invalid file type.
- Email blocked due to the misconfiguration of the recipient’s email server.
Unknown Users
Unknown users are a significant cause of email bounces. Email servers have a variety of error messages for this issue. For example:
- recipient address rejected: User unknown in virtual mailbox table
- no mailbox by that name is currently available
- The following recipient cannot be reached
- no such user
All indicate that the email address you are using is invalid. Typically the email address is incorrect, but an incorrect server configuration could trigger the bounce. Here’s an example of an unknown user error for the Postfix email server:
<[email protected]>: host rackaid-com.p10.mxthunder.com[216.172.106.27] said: 550 5.1.1 <[email protected]>: Recipient address rejected: User unknown in virtual mailbox table (in reply to RCPT TO command)
Unknown Domain
The domain you used in your email either does not exist or cannot be resolved by DNS. Domain errors are less common, and error messages vary considerably, but you may see something like this:
Host or domain name not found. Name service error for name=rackaid.co type=AAAA: Host not found
Email Spam Filtering
Spam filters may block your email. If your server’s IP is on a blacklist or your domain has a history of sending spam, your email may be blocked. Here’s an example of this type of block:
554 5.7.1 Service unavailable; Client host [193.32.160.135] blocked using b.barracudacentral.org;
Point your email administrator to our blacklist removal guides if you see these errors.
Email Policy Filters
In addition to spam filtering, some systems may use policy filters. Policy filters may scan both incoming and outbound emails. For example, a financial firm may scan outbound emails for credit card numbers. We use policy filters to block emails using non-Latin character sets.
If you have a policy filter block, you may see an error like this:
Remote host said: 550 5.7.1 <[email protected]>: Sender address rejected due to policy reasons.
File Attachment Issues
For security and performance, most email servers limit the type and size of attachments. As with email policy filters, this filtering may be both outbound and inbound. The most frequent email bounce is due to too large of an attachment. For example:
<[email protected]>: 552 552 5.3.4 Error: message file too big (state 18)
Misconfigured Recipient Server
Incorrect configuration at the recipient’s server can cause bounces. In this case, you may or may not receive any specific error other than a non-delivery report.
Soft Email Bounces
A soft bounce is typically a temporary failure in delivery. Many email servers do not send notices about soft failures. Email servers use code 421 for soft failures. In most cases, you do not have to do anything regarding a soft failure. The email server retries sending your message. If the message cannot be delivered, the soft bounce becomes a hard a bounce, and the server notifies you of the failure.
Reasons for Soft Bounces:
- There is a temporary network issue.
- The recipient’s inbox is full.
- There is a temporary issue with the recipient’s server.
- The recipient server is using greylisting, a type of spam filter.
Temporary Network Issues
A network issue between your server and the recipient’s server can trigger a temporary failure. Once the network is working, your server sends the email.
Inbox Full
If your email contact has a full inbox, the server may reject the email. Usually, these are temporary failures. Once there is space, the server accepts the email for delivery. In some cases, full mailboxes may result in immediate hard bounces.
Temporary Server Problems
I’ve seen maintenance periods on email services trigger temporary bounces. Once the maintenance is complete, your server delivers the email.
Greylisting
Greylisting is a type of spam filtering that purposefully delays email. When your server tries to send your message, the recipient’s server issues a temporary error (421) response. In the mail logs, these errors usually look like this:
Server error: '451 4.7.1 You are greylisted for 900 seconds
After a few minutes, your server tries to resend the email. This time the recipient’s server accepts the message.
Many spambots do not retry any failed emails, so by initially telling your server to wait, the recipient’s system can limit spam.
Email Bounces Impact Email Deliverability
In email marketing, bounce rate refers to the percentage of emails that bounce when you send to your subscriber list. If you have a high bounce rate, you put your ability to send email at risk.
What’s considered a high bounce rate? According to CampaignMonitor, the benchmark bounce rate is 2%. If your bounce rate remains above 2%, your sending reputation drops, resulting in spam box placement or worse, blacklisting.
Email sender reputation is a score that email service providers assign to an organization’s email. Usually, there is a separate score for your domain and your server’s IP address.
You can use tools like Return-Paths’s SenderScore to check the score they assign to your server’s IP. In our email, blacklist mitigation work, we find that a SenderScore less than 85 significantly impacts your ability to send email to significant service providers.
How to fix an email bounce?
Make sure you have the correct email address. Watch out for simple typos, extra spaces or @ symbols.
If you have a temporary failure, wait, and send a followup email. Your email server should resend the message automatically.
If you have a 550 error (hard bounce), contact your email service provider. Your email provider or administrator can review your bounce and hopefully fix the error. If you provide the email headers from your bounce, your email administrator can usually spot the issue quickly.
If you are blacklisted, check our our series showing you how to remove your IP address from email blacklists.
Getting Email Headers
Your email administrator will often need email headers to understand why an email bounced. How to view the email headers varies considerably between email clients. We will be posting tutorials on how to view headers, so check back soon.
SMTP Error Code Reference
While there are standards, different email service providers and servers may send slightly different codes. Errors in the 500 range are usually for permanent errors while those in the 400 range for temporary errors. Here’s the error codes used by major email service providers:
- Gmail SMTP Error Reference
- Yahoo! Mail SMTP Error Code Table
- Outlook SMTP Error Codes (scroll to bottom)
Summary & Help
This wraps up everything you need to know about email bounces. If you operate a Linux-powered email server and need help, consider our email support services.